WHEN
HISTORY OF MEDICINAL CANNABIS
The cannabis plant has been used in medicine for thousands of years. Learn more about its long journey and how our knowledge about cannabis has grown significantly over the years.
When did people first start using cannabis for medicinal purposes?
Cannabis is one of the oldest plants in the world to be used for medicinal purposes. It is known that cannabis was cultivated in China as far back as 12,000 BC. The first documented evidence of medicinal cannabis dates to about 4000 BC. Medicinal cannabis reached Europe in the ancient times, having been used in the Greek and Roman civilizations. 1
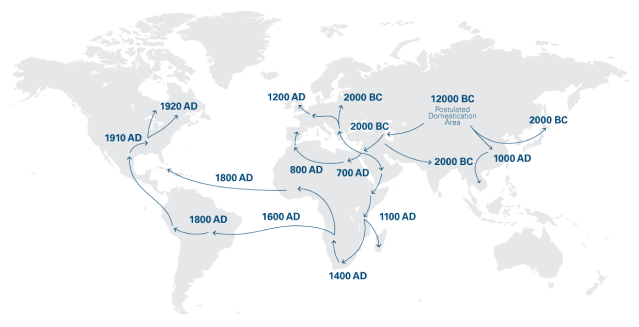
When did medicinal cannabis become a regular medicine?
The therapeutic use of cannabis was first introduced to Western medicine in the mid-1800s when the Irish physician William O’Shaughnessy and French physician Jacques Joseph Moreau separately discovered the benefits of medicinal cannabis while travelling throughout Asia. O’Shaughnessy provided extracts of cannabis to patients and discovered that cannabis had both analgesic and sedative properties. His initial results, followed by those of Moreau and other physicians, led cannabis to spread rapidly throughout Western medicine in both Europe and North America. In fact, the US Pharmacopoeia listed cannabis as a treatment for many conditions into the early 20th century. 1
When was the medicinal use of cannabis abandoned from Western medicine?
During the 1920s and 1930s, two factors contributed to the withdrawal of cannabis as a medicine in the Western world. First, plant-based medicines were unable to deliver the needed quantification of active substances, so the pharmaceutical industry began to develop chemical-based pharmaceuticals. Second, cannabis was becoming stigmatized, particularly in the US, and especially related to its recreational use.1 Ultimately, these two factors led to the inclusion of cannabis in the list of UN Schedule IV substances, together with cocaine and heroin. In December 2020, the UN revised the classification of cannabis, as per the recommendation of the World Health Organization (WHO) that it is a substance with therapeutic value. 2
What have we learned about medicinal cannabis in the past 100 years?
The isolation and identification of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in 1964 was fundamental to the advances in our understanding of the therapeutic properties related to the cannabis plant. Thereafter, in the latter part of the 20th century, various discoveries related to the body’s endocannabinoid system helped explain the mechanistic basis for the therapeutic potential associated with cannabinoids, concretely THC and CBD. The cannabinoid receptors were characterized in 1988 (CB1 ) and 1993 (CB2 ), while the endocannabinoids were discovered in 1992 (anandamide) and 1995 (2-AG). 1 Since then, the amount of research interest in this field has grown tremendously. For example, in 1990, there were about 70 cannabinoid-related publications; that number grew to more than 200 in 2000, more than 600 in 2010, about 2,000 in 2019 and more than 2,500 in 2020. 3
When did medicinal cannabis become legalized?
Medicinal cannabis may have a different legal status in each country. For information about the legalization of medicinal cannabis in certain countries, please follow the links below:

When was the first medicinal cannabis produced?
The history of medicinal cannabis may be different in each country. For information about the production of medicinal cannabis in certain countries, please follow the links below: